一、并发用例场景
对于用户并发编程常用场景有静态资源池、分布式异步调度系统、规则处理引擎、HTTP服务引擎(web服务)及文件处理服务器(如自定义打印服务器)等等,下面举个单例资源调用的例子,如下所示
public class UnsafeLazyInitialization {@b@ private static Object instance;@b@ public static Object getInstance(){@b@ if(instance==null)//线程1访问@b@ instance=new Object();//线程2访问@b@ return instance;//两线程有可能都创建了各自的对象@b@ }@b@}上面代码实现的单例,对于多线程访问的时候,各自cpu处理器在切换各自上下文数据未能及时同步Memory内存中(如下图),可能造成会获取多个对象

二、并发或多线程锁同步
对于大数据处理或多业务流程接口调度都避免不了IO的延时处理等待,通过CPU的并发处理能力将串行IO延时改为并行IO,从而缩短了等待时间,对于并发多线程处理需要解决最多的就是数据状态的一致性问题,这时需要引入锁、Volatile变量、ThreadLocal等方式来同步数据状态。
1. 锁
按照实现方式分为JVM级别实现的Synchronized和JAVA并发包类级别虚拟锁ReentrantLock,具体用法示例可参考“关于线程同步使用synchronized和Lock对比及代码示例”
Synchronized:JVM级别的锁,是JVM的内置属性,可以重入,对于前言中的例子,我们可以加入Synchronized解决问题,如下所示
public class SafeLazyInitialization {@b@ private static Object instance;@b@ public static Object getInstance(){@b@ synchronized (UnsafeLazyInitialization.class) {@b@ if(instance==null)//线程1访问@b@ instance=new Object();//线程2访问@b@ }@b@ return instance;//两线程有可能都创建了各自的对象@b@ }@b@}类在加载时,有把初始化锁,如下图所示
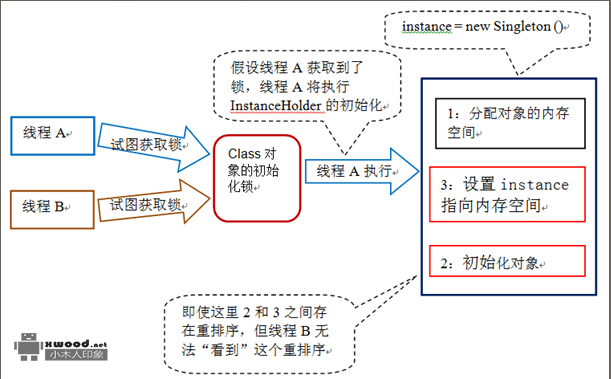
所有对于上面单例,还可以通过类的加载锁来实现,代码如下
public class SafeLazyInitialization {@b@ private SafeLazyInitialization () {@b@ }@b@ private static class InstanceHolder {@b@ public static SafeLazyInitialization instance = new SafeLazyInitialization();@b@ }@b@ public static SafeLazyInitialization getInstance() {@b@ return InstanceHolder.instance; // 这里将导致InstanceHolder类被初始化@b@ }@b@}ReentrantLock: JAVA类库级别的,功能更多:支持等待可中断,公平锁等等
按照公平性分为公平锁和非公平锁
2. Volatile变量
写操作会立即反应到其他线程之中(对一个volatile变量的读,任意线程总是能看到对这个变量最后写入的值);对任意单个volatile变量的读写具有原子性,类似于volatile++这种复合操作不具有原子性
3. ThreadLocal
为每一个使用该变量的线程提供独立的变量副本
/**@b@ * Returns the value in the current thread's copy of this@b@ * thread-local variable. If the variable has no value for the@b@ * current thread, it is first initialized to the value returned@b@ * by an invocation of the {@link #initialValue} method.@b@ * @return the current thread's value of this thread-local@b@ */ @b@public T get() {@b@ Thread t = Thread.currentThread();@b@ ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);@b@ if (map != null) {@b@ ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);@b@ if (e != null) {@b@ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")@b@ T result = (T)e.value;@b@ return result;@b@ }@b@ }@b@ return setInitialValue();@b@} @b@/**@b@ * Sets the current thread's copy of this thread-local variable@b@ * to the specified value. Most subclasses will have no need to@b@ * override this method, relying solely on the {@link #initialValue}@b@ * method to set the values of thread-locals.@b@ * @param value the value to be stored in the current thread's copy of@b@ * this thread-local.@b@ */@b@ @b@public void set(T value) {@b@ Thread t = Thread.currentThread();@b@ ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);@b@ if (map != null)@b@ map.set(this, value);@b@ else@b@ createMap(t, value);@b@}���